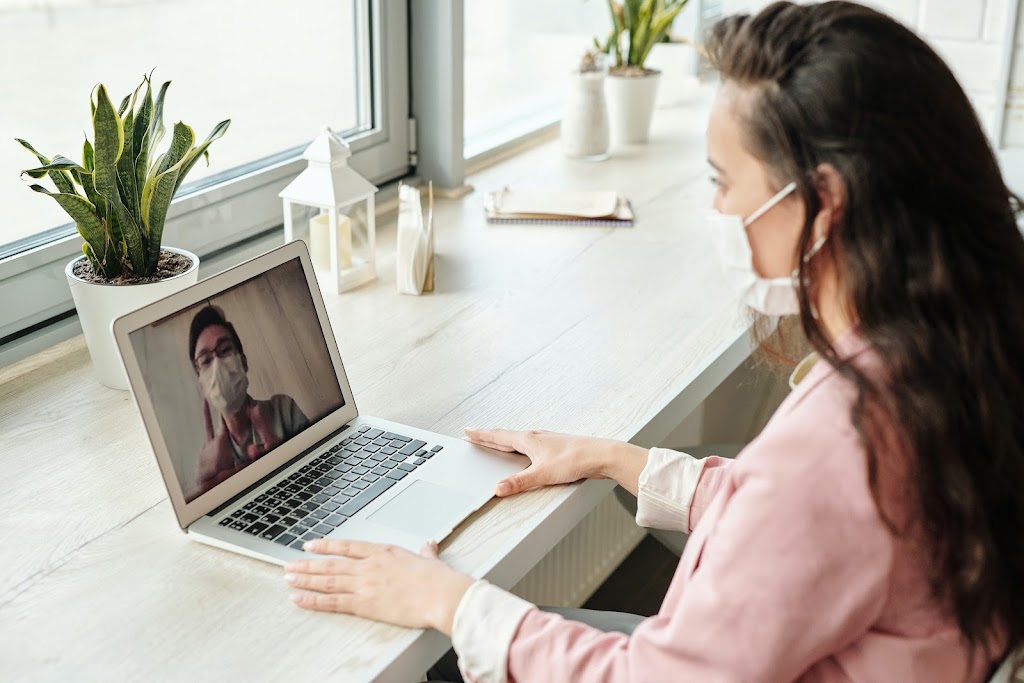
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, and the demand for remote healthcare services continues to grow. From virtual visits and online consultations to remote monitoring and mHealth (mobile health) solutions, telemedicine is changing the way patients receive care.
Telemedicine provides a convenient and cost-effective alternative to in-person medical visits. Patients can access healthcare services from the comfort of their own homes, avoiding the need to travel and reducing the risk of exposure to illnesses. This is especially important during the COVID-19 pandemic, where avoiding in-person contact is crucial for reducing the spread of the virus.
Improved access to healthcare is another key benefit of telemedicine. Patients in remote and underserved areas can receive medical care that they may not have access to otherwise. Telemedicine can also help reduce wait times and improve the efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Data privacy and cybersecurity are critical considerations in the telemedicine industry. Personal health data is sensitive information that must be protected from breaches and hacking. Healthcare providers must implement robust security measures to ensure the privacy and protection of patient data.
In addition to data privacy and cybersecurity concerns, telemedicine also faces the challenge of reimbursement. Insurance companies may not cover telemedicine services, and patients may be responsible for paying out of pocket. There is a need for standardization in telemedicine billing and reimbursement to ensure that patients have access to the care they need.
Despite these challenges, the future of telemedicine looks bright. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see more sophisticated telemedicine solutions that offer even more advanced health monitoring and treatment options. Telemedicine has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach healthcare, making it more convenient, cost-effective, and accessible for everyone.
In conclusion, the demand for telemedicine continues to surge, driven by the need for convenient and cost-effective healthcare solutions. Telemedicine offers improved access to care, particularly for patients in remote and underserved areas. However, data privacy and cybersecurity must be a priority, and there is a need for standardization in telemedicine billing and reimbursement. Despite the challenges, the future of telemedicine looks bright, and we can expect to see continued growth and advancements in this field in the years to come.